Please Be Patient !
The videos and images on this page are HD and take some time to load.
Video Loading..
Introduction
Recap of previous sections covering:
History and origins of powers.
Lawsuit system (complaints, tort laws, contract agreements, case law).
Taxes and mortgages.
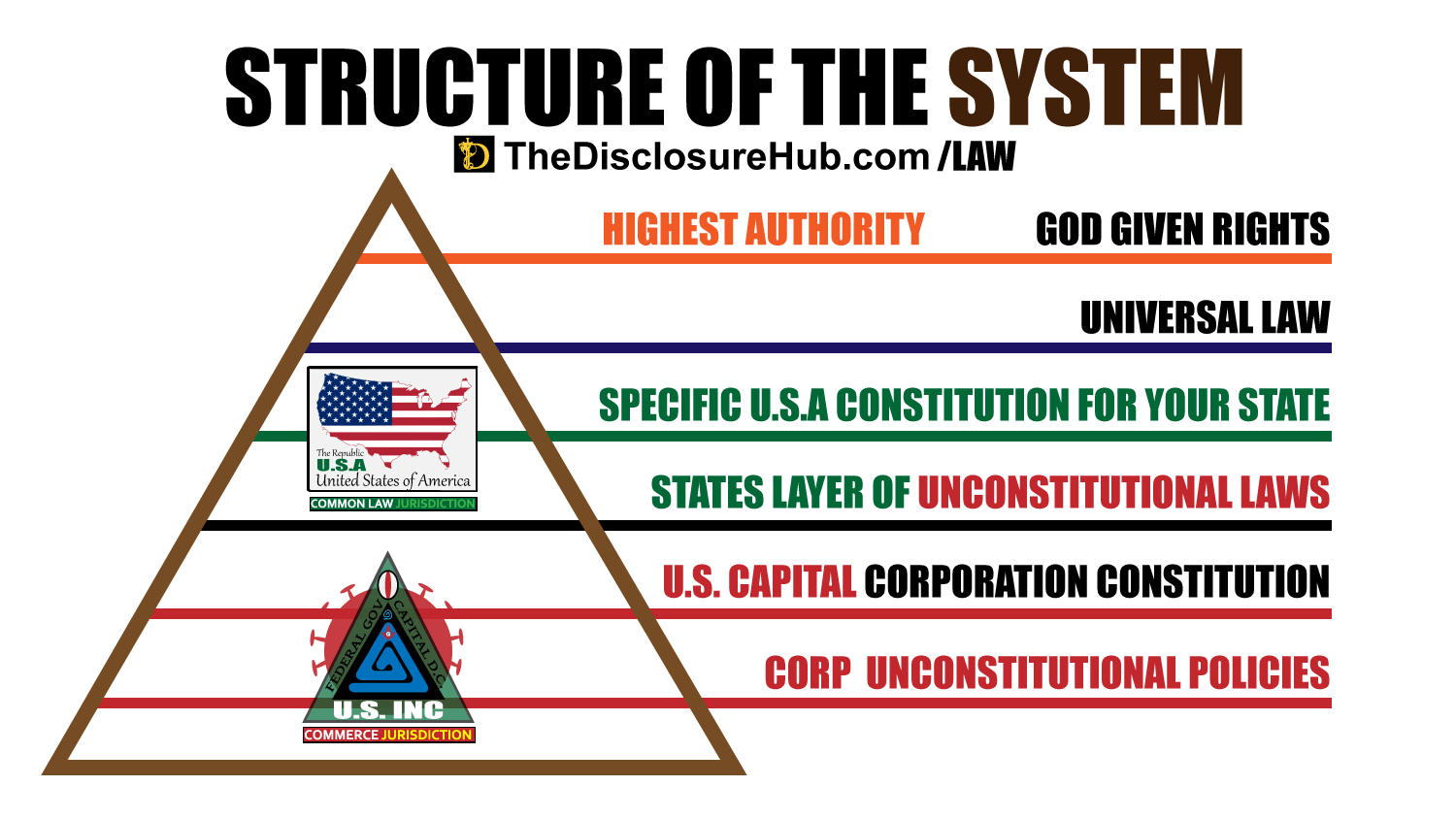
Overview of the system.
Objective of Current Section
Focus on mechanisms for self-defense and activism.
Emphasis on understanding, revisiting information, and becoming fluent with the content.
Metaphor of the Crown
Concept of being a "king" and asking incriminating questions.
Importance of confidence and evidence collection (notes, certification).
Freedom of Information Act (FOIA)
Background and significance:
Enacted on July 4, 1966, by President Lyndon B. Johnson.
Response to scrutiny during the Vietnam War, Watergate scandal, civil rights movement.
Usage:
Obtaining records from federal government agencies.
FOIA requests for body camera footage, government security footage, etc.
FOIA Request Process
Sending detailed correspondence to federal agencies.
Ensuring requests are as specific as possible.
Options to receive data (digital format preferred, possible fees).
Importance of certified mail and evidence collection.
Agencies' response time (20 days, extendable under circumstances).
Remedies for unfulfilled requests (complaints, lawsuits for injunctive relief).
Databases with FOIA returned requests (e.g., WhatDoTheyKnow.com).
Example of FOIA Request
Detailed template for submitting FOIA:
Include date, recipient address, request details.
Request digital format to simplify data handling.
Address possible agency excuses for non-disclosure.
Private Property and Common Law
Protection of private properties (pockets, backpacks, houses, vehicles).
Operating under common law jurisdiction (thick shield).
Suing officials in individual capacity for violations.
Private Member Associations (PMAs)
Concept and power of PMAs.
Creation and operation:
Simple contracts between members.
Can be as detailed as constitutions and bylaws.
Tax benefits and legal defenses.
Real-life example:
Cannabis smoke clubs.
Challenges and considerations for creating enforceable PMAs.
Power of the Press
Press as a constitutional right.
Ability to investigate and gather information.
Using press rights to expose malpractices (FOIA, lawsuits).
Militias
Definition and role:
Defense-oriented groups.
Significance of knowing rights and standing together.
Practical Examples and Tips
Conducting audits (e.g., traffic tickets).
Asking jurisdiction-based questions to challenge authority.
Emphasize continuous learning and verification of information.
Conclusion
Encouragement to apply knowledge and stand up for rights.
Importance of community and collective action.